Analyze compensation data to identify pay inequities
PayParity® analyzes compensation and benefits data directly from your HRIS system to uncover pay inequities across gender, race, age, and more. Conduct proactive or compliance-driven analyses to pinpoint disparities, reduce legal risk, and build trust by ensuring unbiased, transparent pay practices across your workforce in an easy-to-use platform.
Schedule Demo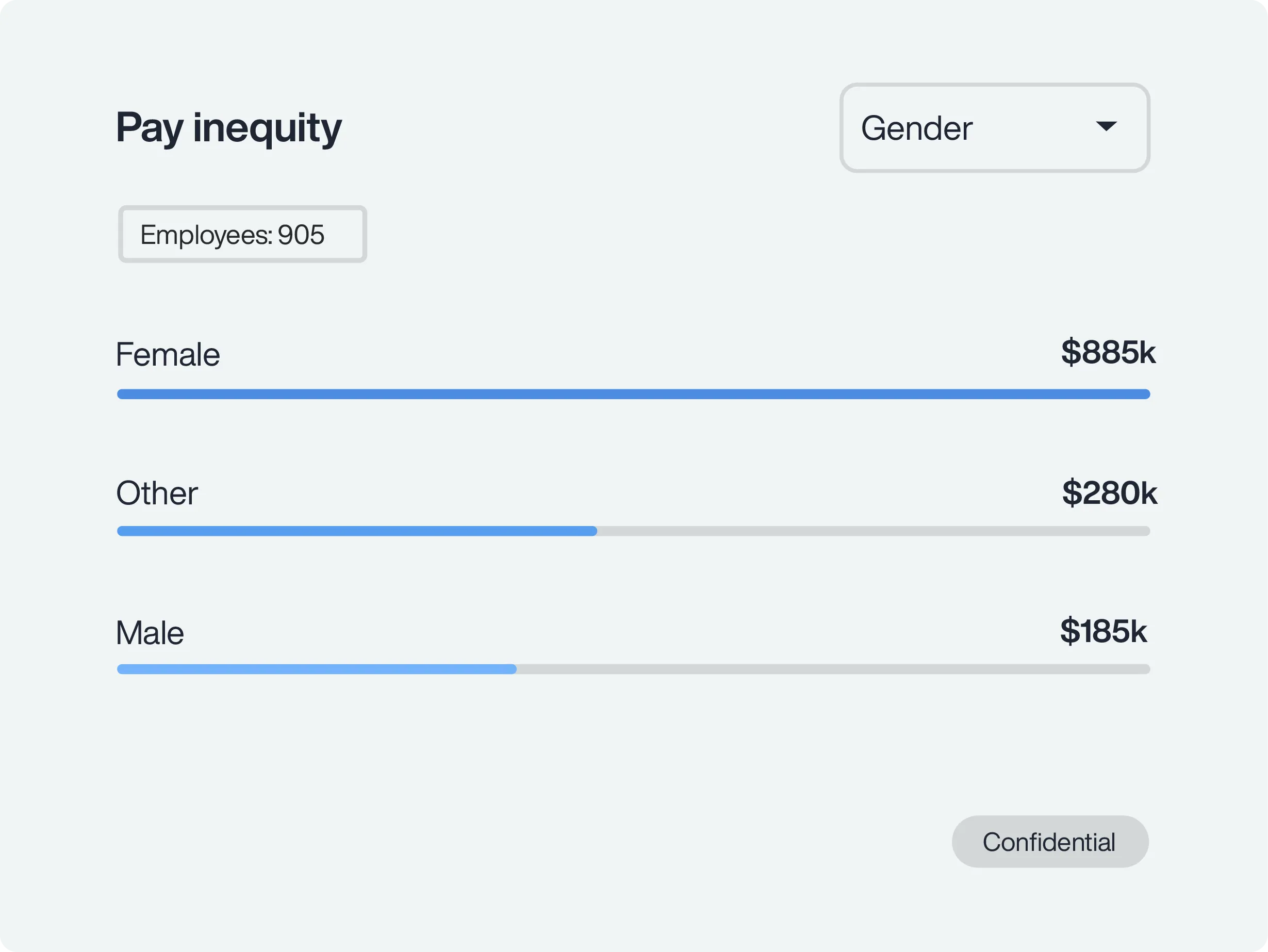
Optimize remediation with AI-powered R.O.S.A.
PayParity’s Trusaic AI-powered remediation agent, Remediation Optimization Spend Agent (R.O.S.A.) helps you remediate pay inequities with precision. R.O.S.A., runs hundreds of simulations to identify the most effective pay adjustments — before any dollars are spent. Trained on the most trusted methodology by global enterprises, R.O.S.A. ensures your remediation strategy maximizes the ROI of your budget.
Learn More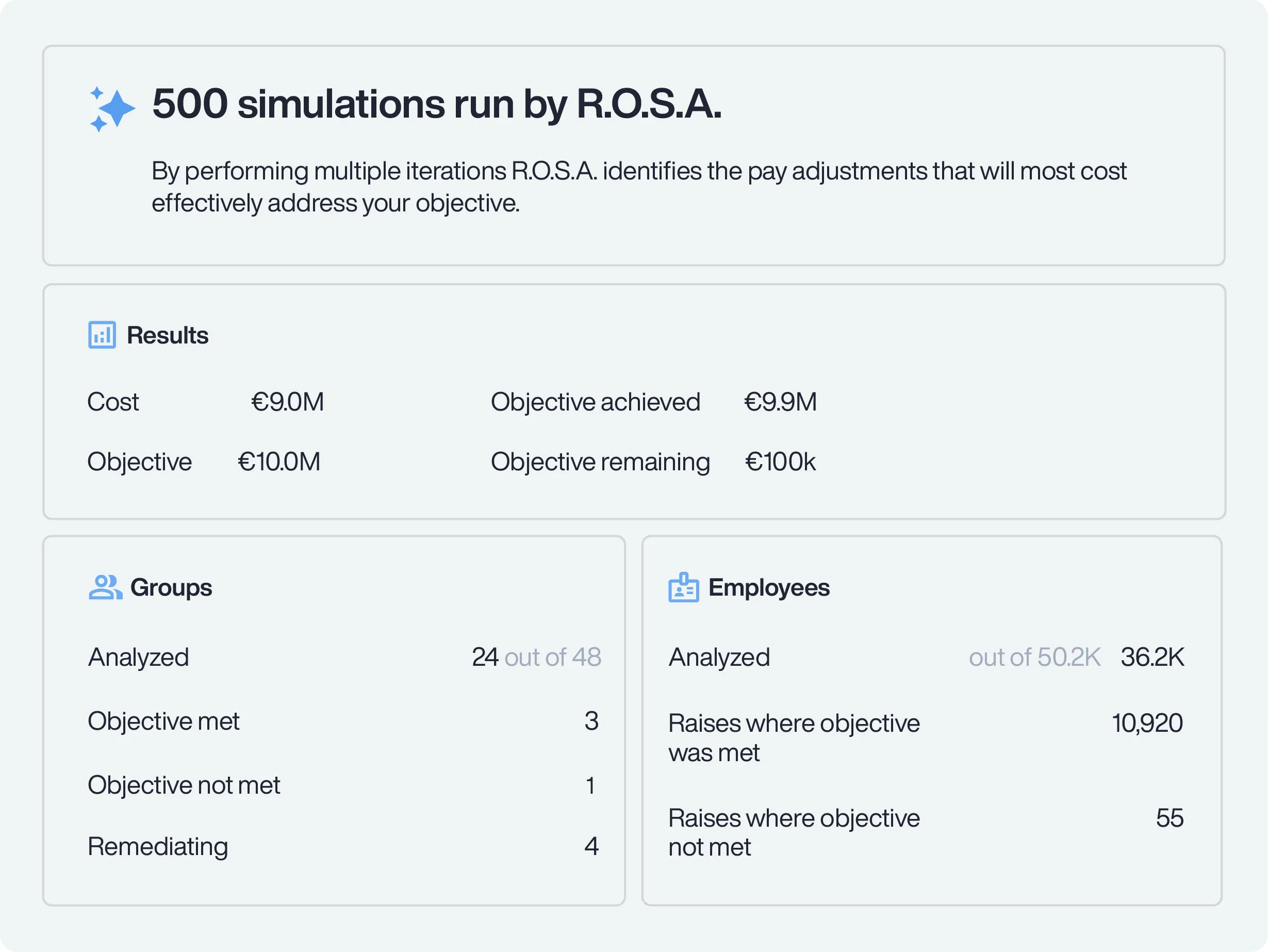
Empower your organization with guided pay decisions
PayParity enables you to prevent future pay inequities by addressing systemic root causes and through the continuous monitoring of your pay practices. Use your pay equity analysis to guide salary decisions with tools like Salary Range Finder®. Keep progress on track by embedding unbiased pay practices into hiring, promotions, and compensation adjustments.
Schedule Demo
Confidently report and comply with global pay transparency requirements
Ensure compliance in any jurisdiction with data-backed pay transparency reporting. PayParity helps you identify pay inequities, implement lasting solutions, and generate accurate reports that meet global standards. Build trust with employees and stakeholders worldwide.
Learn More
Key Features
Global pay equity analysis
Identify pay inequities through ongoing
monitoring to meet transparency
laws and compliance worldwide.
True intersectional analysis
Address pay inequities across gender,
race, age, disability, and more
in one comprehensive analysis.
Legally compliant methodology
Ensure defensible pay equity practices,
avoiding loopholes, pre-set reference
classes, or gamification tactics.
Remediation spend optimization (R.O.S.A.)
Run hundreds of pay analyses at once
to maximize remediation impact and
meet global compliance needs.
EU pay transparency compliance
Close pay gaps over 5% and comply with
EU “right to information” laws to meet
evolving pay transparency requirements.
Global reporting compliance
Create customized pay equity reports
to meet unique compliance requirements
across jurisdictions worldwide.
Capabilities
FAQs
-
How does PayParity help prevent pay inequities?
PayParity provides a comprehensive pay equity analysis across gender, race, age, disability, and more – all in one advanced statistical model. It pinpoints inequities and their root causes, giving you the power to fix the problems at their source and prevent future disparities from occurring.
-
Can PayParity help global organizations achieve compliance?
Yes. PayParity helps organizations achieve pay equity across the globe while ensuring compliance with international pay equity laws. These include but are not limited to:
- EU Pay Transparency Directive
- United Kingdom’s Equality Act
- Canada’s Pay Equity Act and Regulations
- Ireland’s Gender Pay Gap Information Act
- Australia’s Workplace Gender Equality Act
- Brazil’s Equal Pay Act
- South Africa’s Employment Equity Act
- Israel’s Male and Female Workers Equal Pay Law
- Japan’s Act on Promotion of Women’s Participation and Advancement in the Workforce
Our pay equity solution adapts to evolving regulations worldwide, providing seamless support across all jurisdictions.
-
Can PayParity prepare us for the EU Pay Transparency Directive?
PayParity ensures compliance with the EU Pay Transparency Directive by identifying and resolving unexplained pay gaps of 5% or more. It generates jurisdiction-specific reports and helps you confidently meet all deadlines and disclosure requirements.
-
Can PayParity help ensure we pass our U.S. Federal Contractor (OFCCP) audit?
Yes. PayParity supports your Affirmative Action Plans, EEO-1 reporting, and OFCCP audits with unlimited, customized pay equity analyses. Easily tailor reports to meet federal requirements and demonstrate your commitment to merit-based pay.
-
Is PayParity secure and GDPR compliant?
PayParity maintains a comprehensive information security program which contains administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to secure your data, consistent with all applicable data protection laws, including but not limited to GDPR, and applicable federal and state laws, including, but not limited to, the California Consumer Privacy Act, as amended by the California Privacy Act. In addition, we are SOC 2 Type II certified.
-
How does PayParity ensure attorney-client privilege?
You don’t have to sacrifice attorney-client privilege when using pay equity software. To ensure you’re protected, we work with your counsel to maintain attorney-client privilege. Unlike consulting firms which may only be covered by a standard non-disclosure agreement, attorney-client privilege minimizes mandatory disclosure risk.
-
Can PayParity integrate with my identity management system for secure access?
Yes. PayParity integrates with identity access management systems like Okta® to offer optional single sign-on (SSO) for secure and seamless user access. This integration simplifies login processes and strengthens data security. Even without SSO, PayParity maintains SOC 2 compliance and adheres to strict security standards to keep your pay data protected.
-
What is EDGE certification, and how can PayParity help you achieve it?
EDGE certification proves your organization has achieved pay equity through independent third-party verification. PayParity can help you meet the requirements for one of three EDGE certification tiers, demonstrating your commitment to unbiased pay practices. By using PayParity, your pay equity data is accurate, defensible, and ready for certification.
-
What is the Fair Pay Innovation Lab, and how does it validate PayParity?
The Fair Pay Innovation Lab awards the UNIVERSAL FAIR PAY CHECK®, certifying that organizations follow fair pay practices. Trusaic’s PayParity platform is certified by the Fair Pay Innovation Lab, meaning your pay equity analysis will meet their rigorous standards. The lab also provides guidance to help you close unexplained pay gaps and achieve unbiased pay structures.
-
How does PayParity help meet ESG and CSRD reporting requirements?
PayParity provides detailed pay equity analytics that align with ESG reporting standards like the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and Global Reporting Initiative (GRI). The platform collects and organizes data on key ESG metrics, ensuring you meet compliance requirements and show your commitment to sustainable, ethical business practices.
-
Does PayParity help with pay transparency?
Yes. PayParity ensures your compensation practices are fair and compliant, which enables you to leverage our pay transparency tools Salary Range Finder, Regulatory Pay Transparency Reporting, and TrueTransparency to confidently communicate equitable pay ranges and practices to key stakeholders.
-
Is PayParity easy to use for compensation, rewards, and legal teams with no data science background?
Yes. PayParity is designed with a clean, intuitive interface that makes advanced pay equity analysis accessible to everyone. From compensation/total rewards to legal teams, users can navigate dashboards, run reports, and interpret results without needing a data science background. With built-in guidance and AI-powered insights, PayParity turns complex pay equity compliance into a seamless, user-friendly experience.